Annotations
Published: February 10, 2026
Every day, professionals across industries face the same challenge: how to collaborate effectively on documents without losing context, creating confusion, or compromising the original content. A contract needs legal review from three different departments. A construction blueprint requires input from architects, engineers, and safety inspectors. A medical report must be analyzed by multiple specialists before a treatment decision can be made. In each scenario, the solution isn’t just sharing the document—it’s enabling meaningful, traceable collaboration directly on the document itself.
This is where annotations become indispensable. More than digital sticky notes or highlighted text, modern annotations are the infrastructure that powers document-driven workflows in healthcare, finance, legal, government, and engineering sectors worldwide.
Annotations are structured visual and interactive elements that sit on top of digital documents, enabling users to add meaning, feedback, and workflow context without modifying the original content. They are a foundational capability in modern document management systems, powering review, collaboration, approval, and validation workflows across industries.
Annotations exist in multiple categories, including markup annotations for review, shape annotations for visual emphasis, textual notes for commentary, stamps for status indication, measuring annotations for CAD drawings and DICOM images, and eSigning annotations for secure approvals.
Core Categories of Document Annotations
There are three main categories of annotations, each designed to address a specific communication or review requirement:
- Markup Annotations: These annotations help reviewers visually emphasize specific content within a document. Using highlights, underlines, or strikeouts, users can draw attention to important text, flag suggested changes, or mark content for removal.
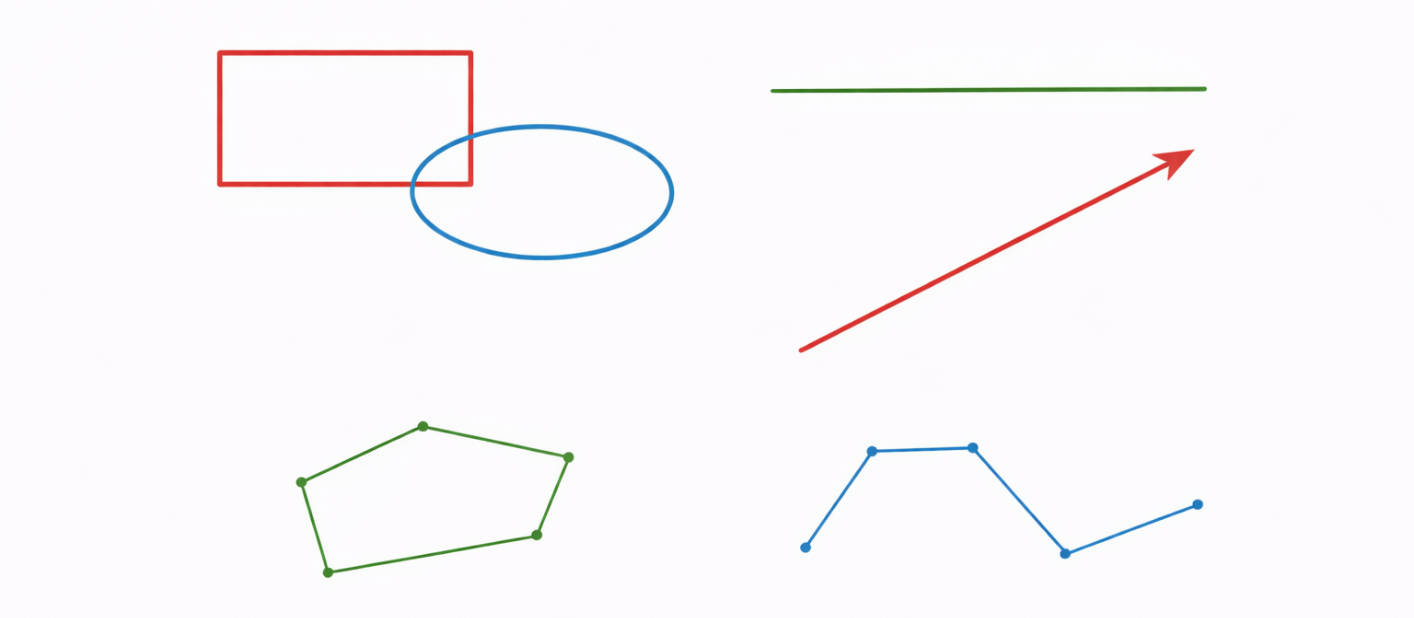
- Shape Annotations: Graphical overlays such as rectangles, circles, arrows, or freehand drawings that visually frame or point to specific areas within a document.
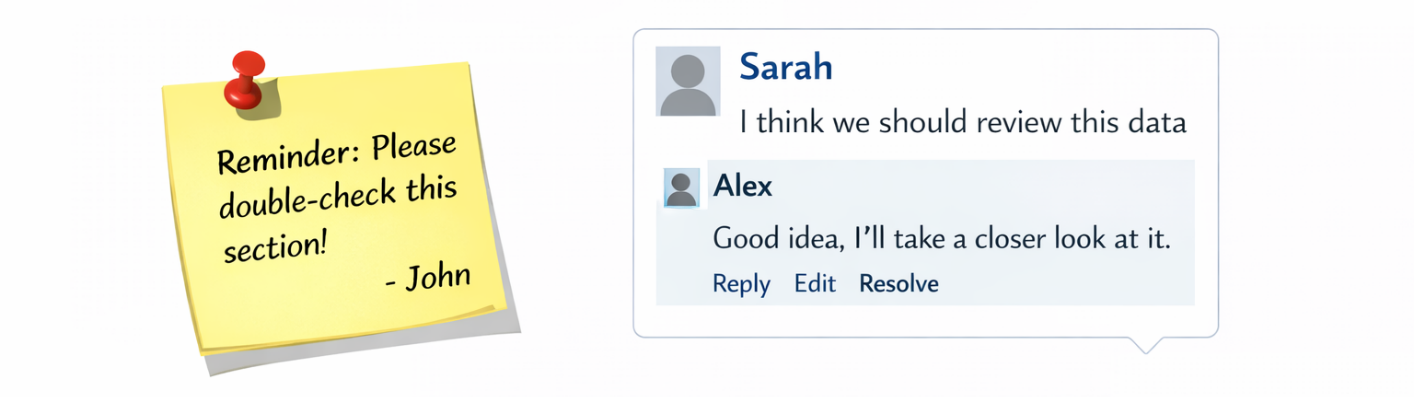
- Textual Annotations: Supplemental text elements, including sticky notes and floating text boxes, that allow users to add explanations, comments, or instructions.
Key Benefits
Annotations greatly improve document-centric workflows by promoting collaboration and clarity, leading to faster and informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Multiple users can annotate the same document concurrently, with each annotation preserved as an independent object.
- Contextual Commenting: Feedback is anchored directly to the relevant content, improving accuracy and reducing ambiguity during reviews, while also allowing reviewers to tag specific users to draw attention, request input, or assign follow-up actions.
- Streamlined Approvals: Status-driven annotations such as stamps, signatures, and checkmarks enable fast, auditable approval cycles.
- Centralized Feedback: All comments, markups, and decisions remain embedded in the document, creating a single source of truth.
- Auditability and Traceability: Annotations retain metadata such as author, timestamp, and status, supporting compliance and accountability requirements.
Use Cases
Annotations are widely adopted wherever documents require collaboration, review, and validation, or decision-making.
- Document Approval Workflows: Organizations use annotations to expedite documents through structured approval cycles.
- Document Review and Quality Assurance: Legal teams, editors, and compliance officers rely on markup annotations to highlight issues, suggest revisions, and confirm accuracy without altering source content.
- Loan and Financials: In financial services, annotations help underwriters flag discrepancies, request additional documentation, and record internal decisions directly on application files.
- Insurance Claims Processing: Claims adjusters annotate reports and images to identify damages, document assessments, and support settlement decisions with visual evidence.
- Healthcare and Medical: Annotations enable collaborative review of medical reports, DICOM image analysis, and treatment planning, while ensuring HIPAA compliance and improving care coordination.
- Government and Public Sector: Annotation systems support legislative and legal reviews, contract evaluations, all while enabling transparent governance, while preserving document integrity.
- Technical and Operational Reviews: Engineering, construction, and manufacturing teams use shape and measurement annotations to review drawings, plans, and schematics with precision.
Annotation Types
Markup Annotations: Markup annotations are designed for review and commentary. Examples include highlights, underlines, strike-throughs, and squiggly lines.
Non-Markup Annotations: Non-markup annotations add interaction and functionality to a document rather than just visual emphasis. They enable actions like navigation, data entry, and approvals. Examples include links, sticky notes, form fields, checkboxes, buttons, and signature fields.
Shape Annotations: Shape annotations visually define regions of interest within a document. They are commonly used to outline sections, indicate areas of concern, or guide attention.
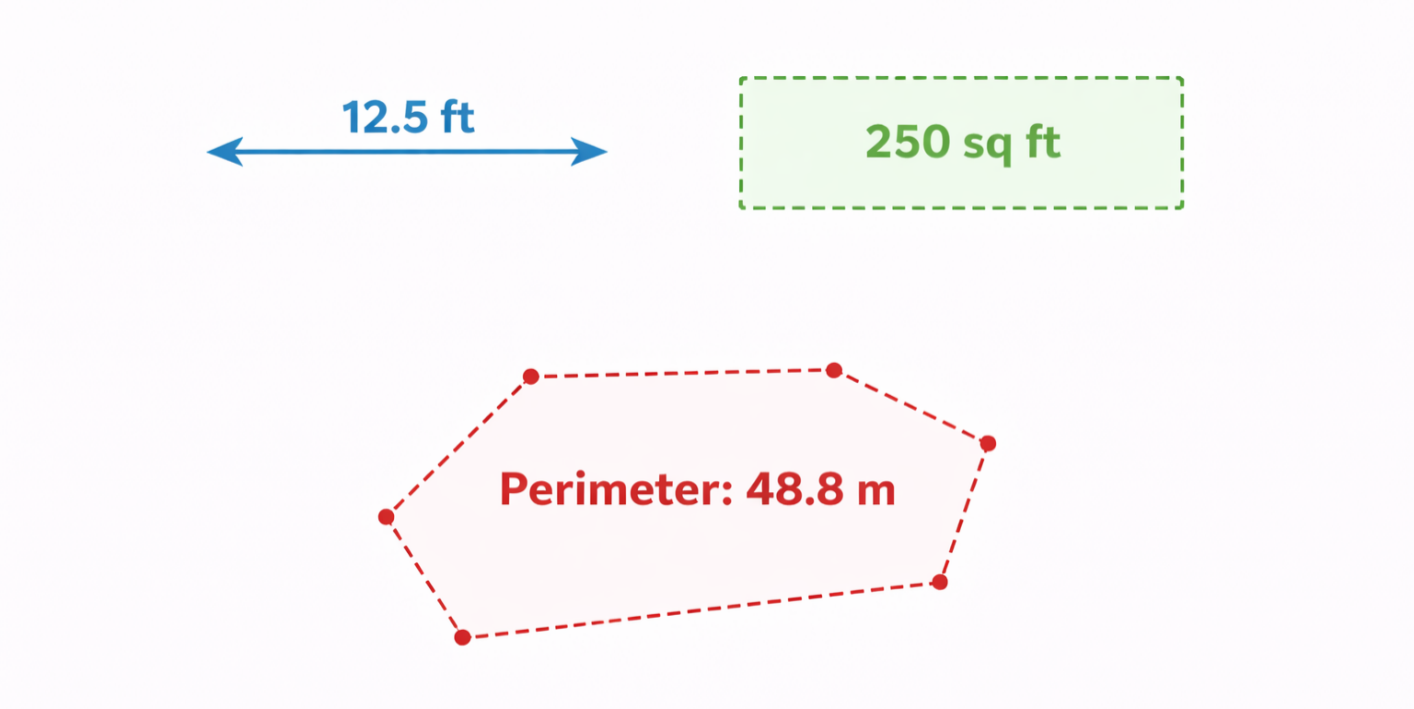
Measuring Annotations: Measuring annotations calculates distances, areas, and perimeters based on document scale. These annotations are essential in medical, design, construction, and inspection workflows.
Detailed Annotation Types:
Markup Annotation Types
Markup annotations are optimized for readability and review efficiency.
- Highlight: Emphasizes important text
- Underline: Draws attention to specific phrases
- Strike-through: Indicates removed or invalid content
- Squiggly: Flags potential issues or errors
Textual Annotations
Textual annotations allow users to add explanatory notes or comments.
- Sticky notes
- Free-text comment boxes
These annotations support threaded discussions and reviewer collaboration.
Stamp Annotations
Stamp annotations communicate document status instantly. Common examples include Approved, Rejected, Draft, and Confidential. Stamps are reusable and can be standardized across organizations.
Shape Annotation Types
Shape annotations provide visual clarity.
- Rectangles and ellipses
- Lines and arrows
- Polygons and polylines
They are often used in audits, inspections, and technical documentation.
Measuring Annotation Types
Measuring annotations supports scale-aware calculations.
- Distance measurements
- Area measurements
- Perimeter measurements
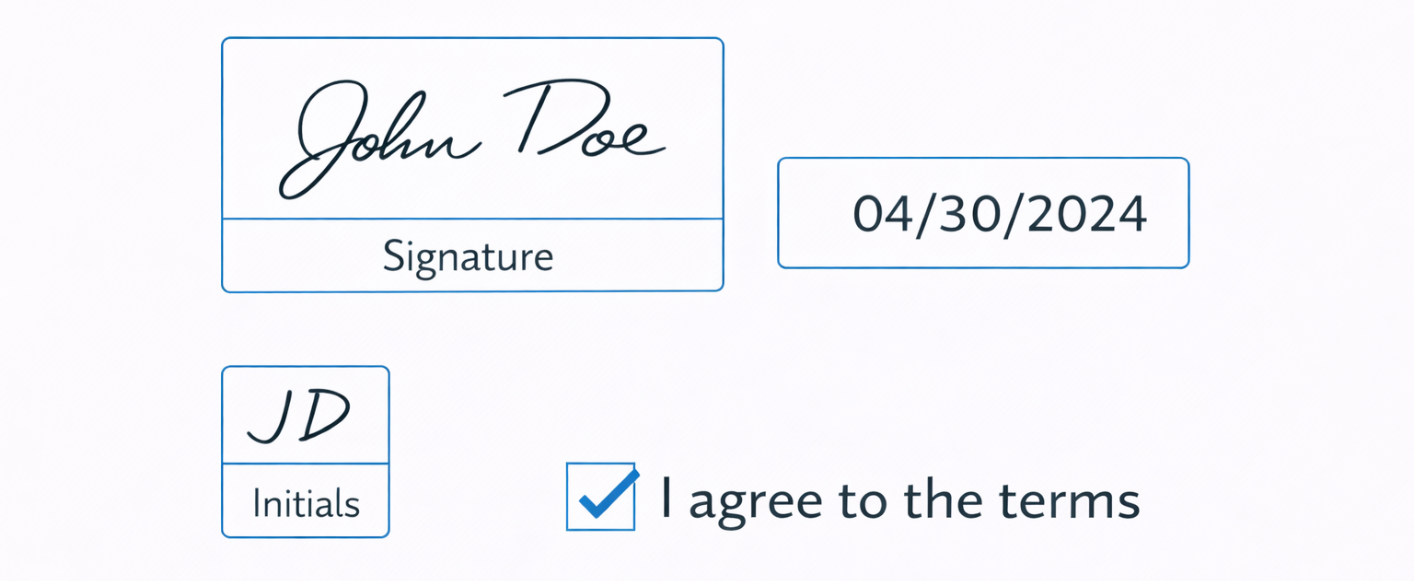
eSigning Annotations
eSigning annotations enable secure digital approvals.
- Signature fields
- Initial fields
- Initial fields
- Date fields
- Checkbox acknowledgements
These annotations integrate seamlessly into digital signing workflows.
Annotation Types and Their Usage Overview:
| Category | Icon | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Markup Annotations | ✏️ | Visual review and emphasis | Highlight, Underline, Strike-through, Squiggly |
| Textual Annotations | 💬 | Add notes and discussions | Sticky notes, Free-text comments |
| Non-Markup Annotations | 🔗 | Enable interaction/navigation | Links, Form fields, Media |
| Stamp Annotations | 🏷️ | Indicate document status | Approved, Rejected, Draft |
| Shape Annotations | 🔲 | Highlight regions of interest | Rectangles, Arrows, Polygons |
| Measuring Annotations | 📐 | Scale-based calculations | Distance, Area, Perimeter |
| eSigning Annotations | ✍️ | Secure digital approvals | Signature, Initial, Date |
MST Annotation Model
The MST eViewer 7 Annotation Model is built utilizing robust JavaScript APIs that allow developers to create, manage, persist, and synchronize annotations programmatically. Annotations are treated as structured data objects rather than simple visual overlays, enabling deep integration with enterprise workflows and external systems.
The Annotation Service is the primary interface for annotations in eViewer 7. It is accessed through the viewer instance and exposes methods that allow applications to:
- Create new annotations (shapes, markup, text, stamps, etc.)
- Retrieve all annotations associated with a document
- Modify annotation geometry and visual properties
- Remove, hide, or filter annotations dynamically
- Add and manage comments and threaded replies
- Control annotation visibility at runtime
In eViewer 7, every annotation is represented as a self-contained annotation object with clearly defined attributes describing its structure, appearance, and metadata.
JSON-Based Annotation Representation
For client–server communication and integration scenarios, annotations are represented using a JSON-based data structure. This format enables annotations to be transmitted over APIs, stored externally, or synchronized across multiple clients. To illustrate, the following code block shows a sample JSON object for a Rectangle annotation:
{
"pageNo": 1,
"annType": "Rectangle", {Annotation Type}
"annCreatorName": "MST",
"currentDate": "1/30/2026",
"currentTime": "3:32:41 PM",
"borderColor": "#FF0000",
"opacity": "0.5",
"borderWidth": "5px",
"fillColor": "#96FEFE",
"rotateWithPage": true,
"borderOpacity": "0.5"
}
PDF Annotations
PDF annotations are natively supported by the PDF specification and include markup, comments, stamps, form fields, and signatures. These annotations are embedded within the PDF file structure and can be interpreted by compliant viewers.
The MST eViewer platform fully supports rendering and interacting with standard PDF annotations. Additionally, PDF-native annotations can be transformed into the platform’s internal PDF annotation model, allowing easy annotation handling, unified behavior, and cross-format consistency.
Developers can manage PDF annotations through dedicated APIs present in the built-in PDF annotations library, enabling creation, editing, deletion, and export operations.
Non PDF Annotations
Beyond PDF, the modern annotation platform supports annotation formats associated with image-based and legacy documents.
TIFF Annotations
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) annotations are commonly used in scanned-document workflows. They enable highlights, shapes, and notes on image files where text content may not be selectable.
WANG Annotations
- WANG annotations are legacy formats still present in some enterprise document repositories. Supporting these annotations ensures backward compatibility and seamless migration.
- In the TIFF specification, the WANG Annotation data (used for legacy annotations created by older imaging/annotation packages such as Imaging for Windows/WANG) is stored in a private TIFF tag with ID 32932 (hex 0x80A4). This tag is not part of the baseline TIFF spec but has become a well-known private tag for embedding Wang-style annotations.
- Tag number: 32932
- Hex ID: 0x80A4
- Tag name: Wang Annotation (annotation data)
With eViewer 7, you can render WANG annotations present in your images. Developers can manage these annotations through dedicated APIs present in the built-in TIFF WANG annotations library, enabling creation, editing, deletion, and export operations.
TL / MO:DCA Annotations
- TL (or T_L) annotations, which is an IBM-proprietary binary annotation format, are mostly associated with MO:DCA documents. MO:DCA documents were widely used with IBM ECM systems including Content Manager and is a subset of the AFP printing format.
- Unlike formats such as TIFF, where annotations are written directly into the document stream using defined tags, MO:DCA TL annotations are stored in a separate binary file. Document viewing applications read these annotation files and overlay the annotations on top of the document during rendering.
- eViewer has deep expertise in managing MO:DCA annotations through its long-standing integration with IBM Content Manager. The platform provides comprehensive capabilities including:
- Native rendering and display of MO:DCA annotations
- Bidirectional conversion between MO:DCA and other annotation formats
- Full read, write, and edit operations with persistent storage
- Preservation of annotation fidelity during format migrations
This support ensures organizations with legacy IBM systems can maintain their existing annotation workflows while gaining the flexibility to integrate with modern document management platforms.
Annotations have evolved from simple margin notes to powerful, programmable tools that drive enterprise workflows across industries. Whether you’re streamlining document approvals, coordinating healthcare reviews, or managing complex engineering projects, a robust annotation system transforms static documents into dynamic collaboration hubs. By supporting multiple annotation formats, from modern PDF annotations to legacy T_L, MODCA, WANG, and TIFF formats, the MST eViewer 7 ensures organizations can leverage their entire document archive while building for the future.
Ready to transform how your organization collaborates on documents? Explore MST eViewer 7’s comprehensive annotation capabilities and discover how programmable, standards-based annotations can accelerate your review cycles, improve compliance, and create a true single source of truth for your document workflows. Contact our team for a demo or start your free trial today to see the difference powerful annotations can make.